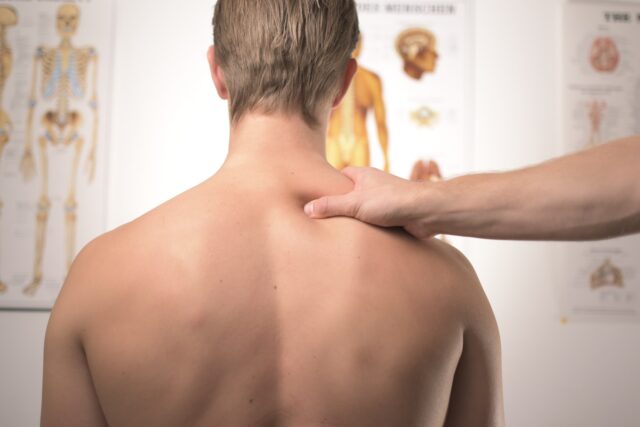
Chronic pain is continual pain that typically has an extended duration over 12 weeks. In contrast, acute pain can warn you about a current injury or illness that you have, and this type of pain does not last long. However, it can become chronic pain if it persists for many months.
Chronic pain affects about one-fifth of American adults and can be caused by a number of different things, such as chronic diseases, autoimmune disorders, a joint or muscle injury, and issues with the nervous system. If you’re looking for specialized care and treatment for chronic pain, consider visiting the Marietta Neuragenex clinic. They have a dedicated team of experts who are well-versed in addressing the various underlying causes of chronic pain and providing personalized treatment plans.
Here are five of the most common chronic pains along with their causes and treatments for them.
1. Back Pain

Based on a study performed by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, roughly 84% of American adults are likely to suffer from chronic back pain during their lifetime.
It typically is situated in the lower back and is commonly caused by these:
- Bulging discs from lifting or twisting incidents
- Abnormal deformities of the spine
- Spinal stenosis, which is the compression of back nerves and the spinal canal
To alleviate this type of chronic pain, you can perform some of the following techniques:
Physical Therapy
Exercise is a common way to treat chronic back pain. For it to work properly, the exercises that you perform should be suited to the symptoms that you are experiencing, and you need to maintain an exercise routine. Some exercises in physical therapy may involve stretching, flexibility, pain tolerance, core workouts, and aerobic exercises.
There are also orthopedic supports that can reinforce the things you work on in physical therapy while also providing short-term relief. ScripHessco has a variety of orthopedic products depending on the type of pain you suffer from.
Mindfulness Practices
Your mental health is crucial when it comes to dealing with chronic back pain since it can result in depression or irritability. You can go to a rehabilitation psychologist to receive strategies for relaxation, such as yoga or meditation, which can help soothe your mind from your current pain.
Dieting
Some foods that have a high quantity of refined sugars and trans fats can cause major inflammation in the back. Reducing these foods and sustaining a healthy weight can help alleviate the pressure and stress on your back.
2. Headaches
Based on a study performed by the Lancet, about 50% of adults have headaches during the year, but at least 90% have a history of headaches over their lifespan. Chronic headaches have a frequency of about 15 days per month for three contiguous months.
These are the main types of headaches and their causes:
- Tension headaches – stress, fatigue or sleeping improperly
- Headaches from eye strain
- Migraines – hormones or issues with the nervous system
- Cluster headaches – blood vessel enlargement from inflammation
- Medication overuse headaches – excessive use of pain medication
Other causes for chronic headaches can include infections, an imbalance in pressure inside your cranium, a brain tumor, or a traumatic brain injury.
There are plenty of treatments that can help ease chronic headaches and their pain:
- Get the required amount of sleep that you need and develop a healthy sleep schedule.
- Reduce your consumption of caffeine since it can trigger headaches.
- Keep a journal about what can trigger your headaches and how long they last.
- Perform aerobic exercise on a routine basis since it can reduce stress.
3. Joint Pain
This type of pain can be caused by multiple different things, such as aging, an infection or an injury. Based on a study done by the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative, arthritis is the most frequent cause of chronic pain, and it has impacted at least 51 million Americans.
These are some of the main causes of chronic joint pain:
- Osteoarthritis, which occurs more frequently among the elderly and impacts larger joints
- Rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune disorder that causes swelling in the joint cavities
- Repetitive motion, which can cause inflammation and occurs mostly among athletes
- Bursitis, which happens when the fluid-filled sacs that surround the joins swell
- Tendinitis, which happens when join tendons go through inflammation
To treat this type of chronic pain, here are some treatments that you can use:
Take pain medication that can alleviate inflammation and swell in the joints. Follow an intermediate exercise routine that does not cause too much stress on the joints. Stretch before you exercise so that you can expand your flexibility in the joints. Try to maintain a healthy weight so that you can reduce joint stress.
4. Nerve Pain
Nerve pain can occur as a result of the nerves being damaged due to drugs or activities that can strip the nerves of their myelin sheath, which is their protective coating. Based on a study conducted by the Mayo Clinic School of Medicine, roughly one-tenth of Americans live with chronic nerve pain.
These are some types of neuropathic or nerve pain and their causes:
- Sciatic, which can cause shooting pain in the leg due to nerve compression
- Diabetic neuropathy, which mostly happens in the hands or feet and happens because of high blood sugar
- Carpal tunnel, which happens with repeated motion
Neuropathic pain can be treated with the following:
- Antidepressants, which can reduce pain from nerve damage
- Anticonvulsants, which are medications that can prevent faulty transmissions with the nerves from occurring
- An implantable device, which can monitor nerve activity throughout your body and transmit electrical signals
Physiotherapy such as massage therapy, which can ease the pain by releasing tension in the muscles, reducing the compression of the nerves, and improving blood circulation in the surrounding area.
5. Psychogenic Pain
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5jc9XZ1n9TY
This type of pain is a disorder that is related to psychology. Some mental problems, such as anxiety, emotions, or fears, can result in the increase of existing pain and extend the duration. Someone who exhibits chronic psychogenic pain frequently experiences pain in an area of the body without true symptoms.
Some treatments for psychogenic pain include these:
- Psychotherapy
- Non-narcotic painkillers
- Antidepressants